
Appetite Control with Semaglutide: A Surgeon’s Insight
If you are on the Gold Coast hearing all the buzz about weight loss injections, you have probably come across semaglutide. Originally developed to help
Discover World-Class Bariatric Care with Dr. Harald Puhalla: Decades of Surgical Expertise Transforming Lives for the Better

Dr Puhalla has a special interest and extensive experience in bariatric procedures, and is dedicated to helping you achieve the best long term outcome possible.
Keyhole surgery is Dr Puhalla’s preferred method to treat a variety of conditions, including hernias, gallstones, reflux, liver and pancreatic disease.
Dr Harald Puhalla is a General Surgeon based on the Gold Coast, Queensland. With over 20 years of experience, his specialty interests include bariatric, hernia, gallbladder, hepato-biliary pancreatic and upper gastrointestinal surgery.
During a sleeve gastrectomy (SG) a narrow gastric tube is fashioned in-between the food pipe (oesophagus) and the small bowel, while the majority of the stomach (80%) is removed. The continuity of the stomach is not interrupted compared to a bypass procedure-
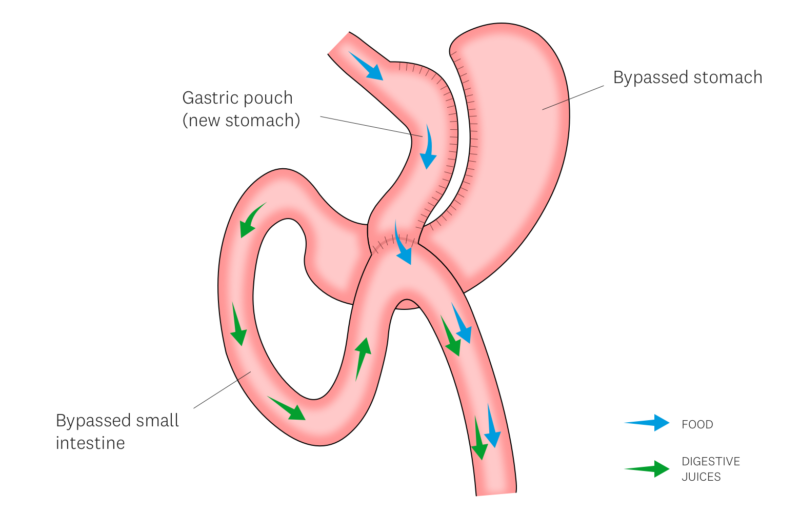
By completely dividing the upper part of the stomach a small gastric pouch is formed, which results in a drastic reduction of the gastric volume. Further a bypass of the first section of the small bowel is created.
By completely dividing the upper part of the stomach a small gastric pouch is formed, which results in a drastic reduction of the gastric volume. Further a bypass of the first section of the small bowel is created during which the bilio-digestive enzymes joining the digestion of the nutrients about 1.5m downstream after the stomach.
The Loop Duodenal Switch (SADI-S or SIPS) combines a moderate restriction (reduced portion sizes) of a sleeve gastrectomy with a moderate reduced absorption (bypassed small bowel).
Revision surgery involves either the conversion of one weight loss procedure into another, in a single or two stage process, or adjusting a previous procedure. This can be due to different factors, including inadequate weight loss or gradual weight gain, or reflux.
The Intra-gastric balloon, is a non-surgical weight-loss procedure which involves the insertion of a specialised balloon inside the stomach to occupy space and limit the food carrying capacity of the stomach.
The only effective form of treatment for a hernia is surgery. Depending on the type of hernia, surgery can be either laparoscopic or open. Both types of surgery are performed under general anaesthetic.
The liver is the largest gland in the human body and is located in the right upper abdomen. The liver has an essential role in: digesting nutrients, detoxification, production of blood proteins, immune response.
The gallbladder is a small pear shaped organ attached to the liver. Bile produced by the liver is stored in the gallbladder between meals before being released into the small intestines during a meal.
Bile ducts are tubular structures connecting the liver with the small bowel. Bile flows from the liver through these ducts via the gallbladder into the small intestine.

Located in the upper abdomen behind the stomach and the intestines, the pancreas is divided up into 3 sections: the head, body and tail.
The pancreas has two major functions: Exocrine: production of enzymes for digestion of food, Endocrine: production of hormones, including some that regulate blood sugar.

Dr Puhalla’s practice is located in the Pacific Private Clinic, in Southport on the Gold Coast. He performs surgery at the Gold Coast Private Hospital and Pindara Private Hospital.
We offer in-person and telephone consultations to all of our patients.
Ultrasound utilises ultrasonic sound waves and the computer creates an image of the organs examined from the reflected ultrasound waves. This test is good at assessing the gallbladder or bile ducts for stones and can detect initial evidence of a liver or pancreas tumour.
For this test, X-rays are used and a computer-generated cross-sectional image of the body is formed. In case of underlying cancer the CT helps to assess how far the cancer has advanced, how many tumours there are, how large the tumours are and whether they can be surgically removed.
Nunc non blandit massa enim MRI uses magnetic rays. This test, similar to CT, can provide very detailed images of liver and pancreas tumours.nec dui nunc mattis. Viverra nam libero justo laoreet sit amet cursus sit amet. Nunc sed augue lacus viverra vitae congue eu.
This technology utilises the fact that most cancer cells are more active than other cells. This causes the cancer to absorb sugar more rapidly than normal cells. A small dose of radioactive sugar is injected into a vein and areas of tumour cells are highlighted on the PET scan. PET can be used in combination with CT scans.
A specialist (gastroeneterologist) puts a flexible tube through the oesophagus, stomach and the top part of the small intestine. On the tip of the tube is a small ultrasound probe which creates imaging of the intestine and specifically the pancreas. If necessary tissue samples can be taken from lesions in the stomach or pancreas. For this procedure the patient is under sedation.
A small flexible tube is advanced into the top end of the small intestine (duodenum) to view the bile ducts, gallbladder and sometimes the pancreatic duct. X-rays are used during the ERCP to help visualising the structures. Minor surgery can be carried out during an ERCP. For this procedure the patient is under sedation.
Laparoscopy can be used to avoid unnecessary more invasive surgery in selected patients. A camera (laparoscope) is passed via a small incision into the abdomen to view the liver and surrounding organs. Instruments can be inserted to take tissue biopsies. Laparoscopy is done under general anaesthetics.
This is a small sample of tissue or fluid from the tumour site, which is sent to a pathologist to examine under a microscope. In general a biopsy is not performed as a first test in liver lesions as we can usually determine the diagnosis by using several different imaging techniques. In pancreatic or bile duct tumours biopsies are more likely to be used.

If you are on the Gold Coast hearing all the buzz about weight loss injections, you have probably come across semaglutide. Originally developed to help

When people hear about GLP-1 medications, they often picture dramatic weight loss and newfound confidence. Across the Gold Coast, these weight loss medications have become

When people think about weight loss surgery, they may not realise that working with a Gold Coast weight loss surgeon can unlock long-term health improvements
When it comes to managing type 2 diabetes, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery (RNYGB) opens a doorway to long-term remission and renewed vitality. This life-changing bariatric

The majority of people focus on nurturing themselves post-surgery. However, building your immune system is something that must start months before the first incision is

Obesity is more than a number on a scale. It is a multifaceted health condition that impacts every area of life, from physical well-being to